California State Maps
These maps show California State Counties, Cities, Federal Areas, Physiographic, and Ecoregions.

California Counties Interesting Facts
California has 58 counties. Most county lines in the interior follow the U.S. Public Land Survey System’s rectilinear grid, while many coastal and earlier-settled areas reflect older Mexican land-grant (rancho) boundaries and natural features. See the CSAC overview, the BLM history of PLSS, and Newberry’s county-boundary commentary.
- Number of counties: 58 (CSAC)
- First & last established: 27 original counties in 1850; last created was Imperial County in 1907. Chronology: Newberry Atlas
- Borders mostly set up by: PLSS township-range lines inland (BLM), plus natural features & historic ranchos (Newberry)
- Highest & lowest county (elevation): Highest point at Mt. Whitney on the Inyo–Tulare line; lowest at Badwater Basin in Inyo County (USGS, NPS)
- Most & least populated county: Most: Los Angeles County; Least: Alpine County
- Least & most developed (proxy = population density): Most dense: San Francisco County; Least dense: Alpine County
- Most geographically diverse county (reasoned pick): Los Angeles County (Pacific beaches, Channel Islands access, coastal plains, the beaches/harbors, San Gabriel Mountains, and Mojave Desert’s Antelope Valley)
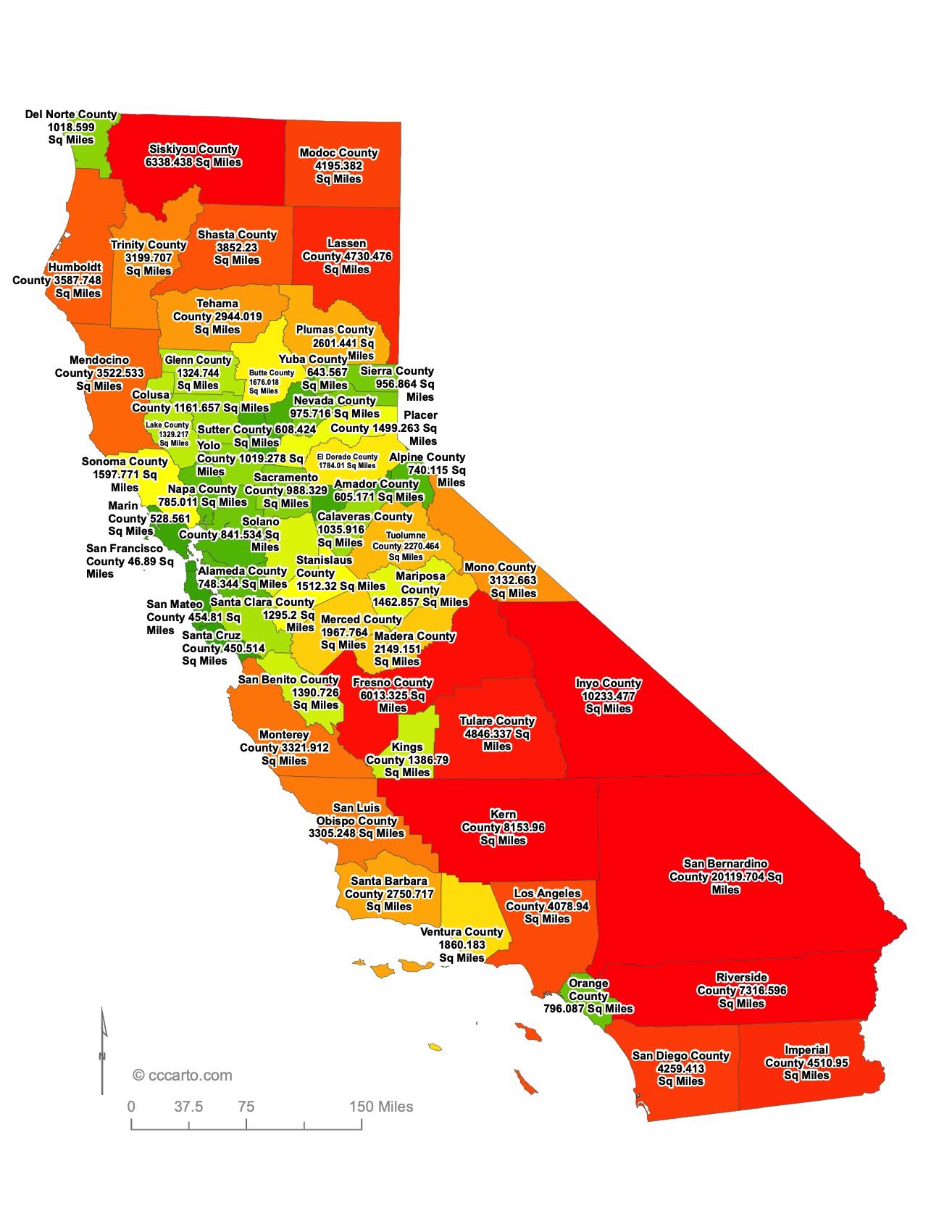
California State County Sizes Map
Smallest County in California State
Alpine County: 740 sq miles
Largest County in California State
San Bernardino County: 20,119 sq miles
Mean and Median Area of Counties in California State
Mean Area: 3057 sq miles
Median Area: 1311 sq miles
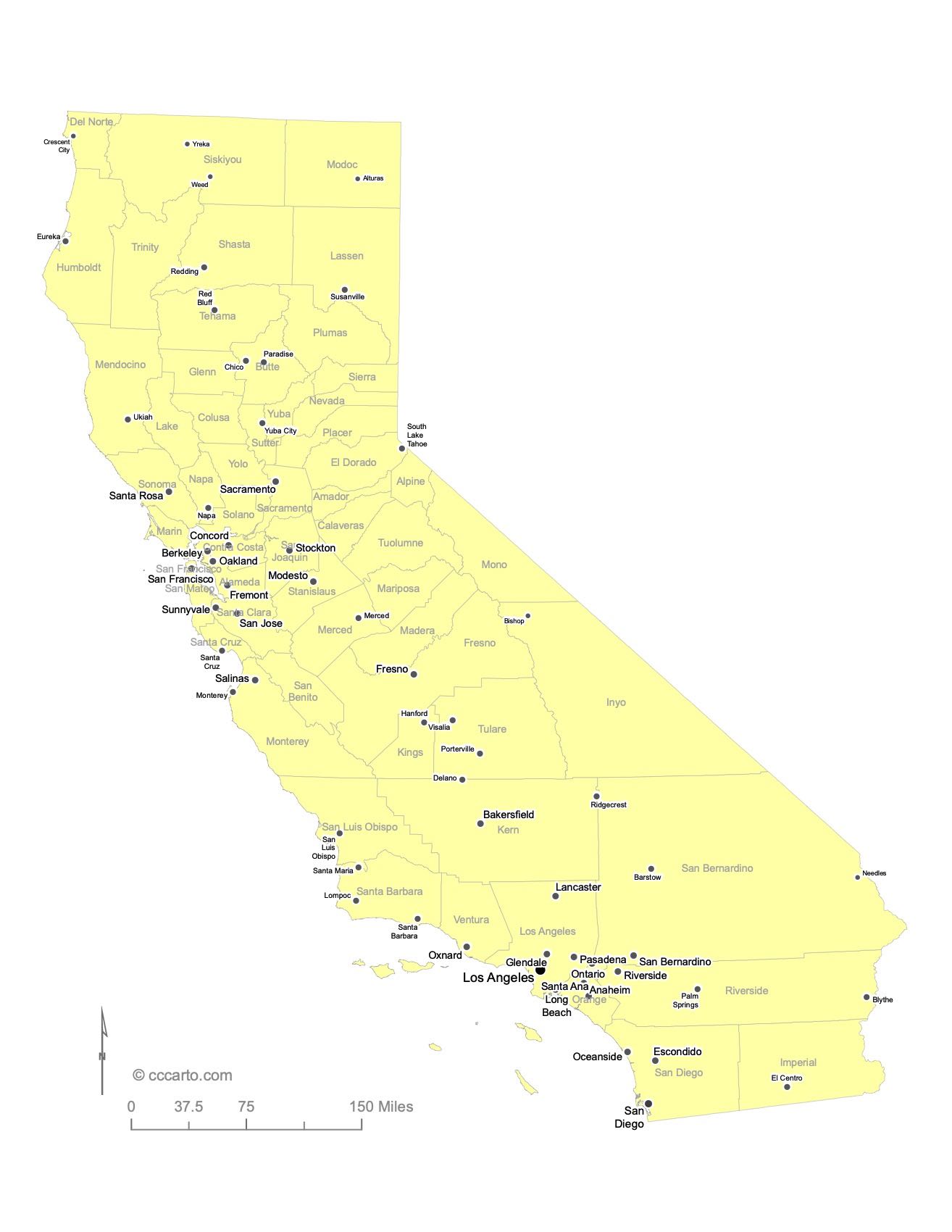
Major Cities of California State and Their Locations
1. Coastal Cities
Los Angeles: The largest city in California, located on the Pacific Coast and a major global hub for entertainment, culture, and trade.
San Francisco: Known for its iconic Golden Gate Bridge, San Francisco is a major city on the northern California coast, famous for its tech industry and history.
2. Inland Cities
Sacramento: California’s capital city, located in the Central Valley. Sacramento has a rich history dating back to the Gold Rush era.
Fresno: A key agricultural hub located in the Central Valley.
Topographic Tour of California
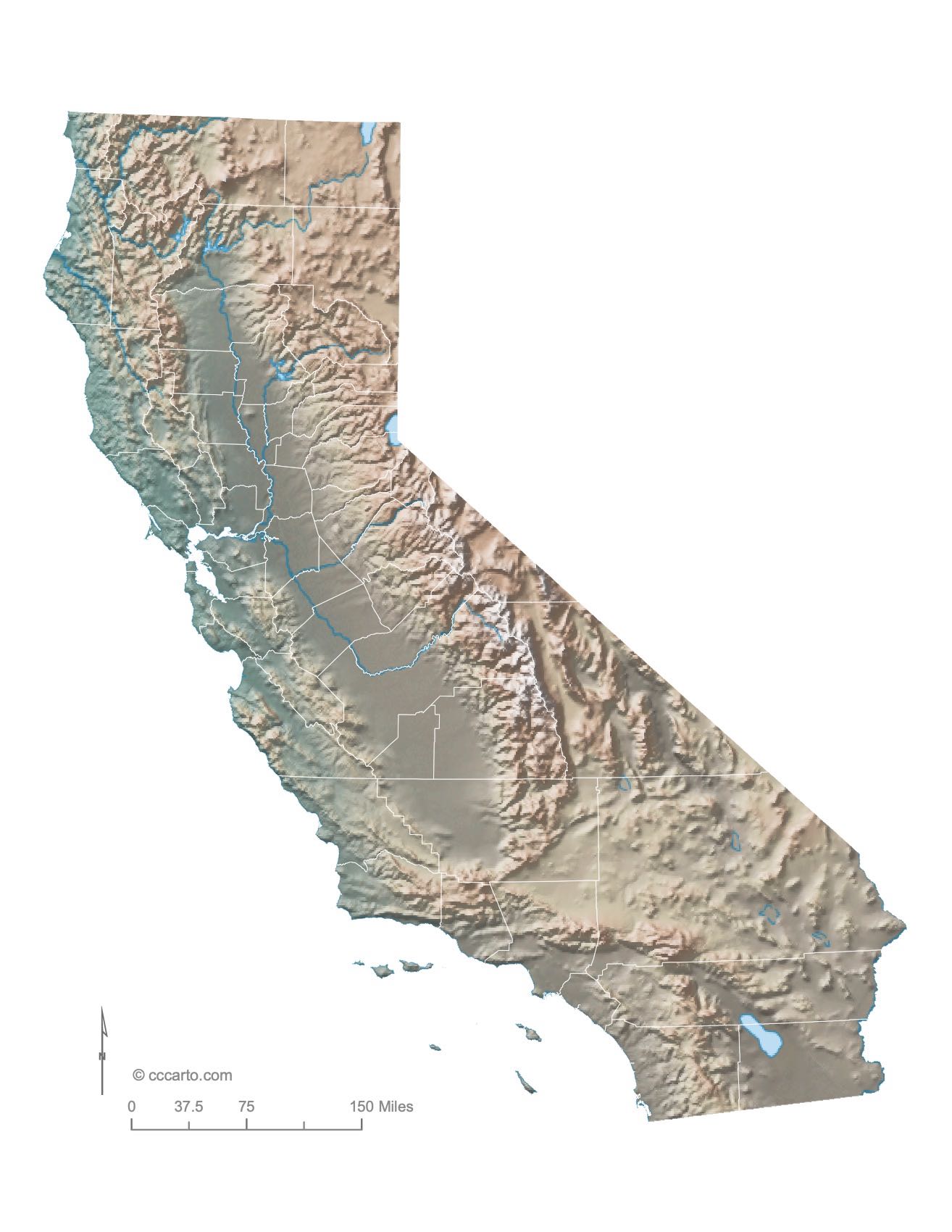
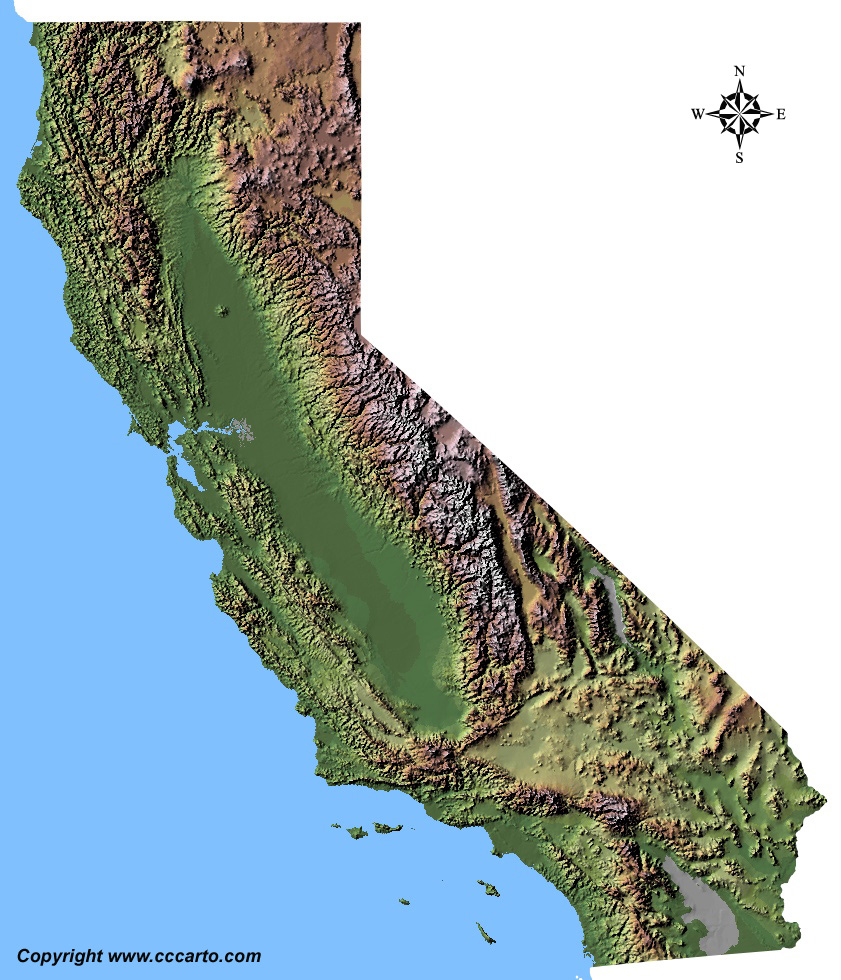
1. Coastal Lowlands
The western edge of California features low-lying coastal areas along the Pacific Ocean. This region includes beaches, estuaries, and coastal hills, especially around the cities of Los Angeles and San Diego.
2. Sierra Nevada Mountains
Running north to south along the eastern edge of California, the Sierra Nevada is home to Mount Whitney, the tallest peak in the contiguous U.S. The range also features Yosemite National Park and Kings Canyon National Park.
3. Central Valley
The Central Valley is a vast, fertile flatland that lies between the Sierra Nevada Mountains and the Coast Ranges. It is one of the most productive agricultural regions in the world, producing a large portion of the nation's fruits, vegetables, and nuts.
4. Mojave Desert
The Mojave Desert in southeastern California is an arid region known for its dramatic landscapes, including sand dunes, Joshua trees, and unique rock formations. Death Valley, the hottest place in North America, is located in this desert.
5. Cascade-Sierra Range
Stretching through the northern parts of California, this mountain range is characterized by volcanic peaks such as Mount Shasta and Lassen Peak. It forms part of the Pacific Ring of Fire and contains dense forests and pristine alpine lakes.
6. Klamath Mountains
The Klamath Mountains, located in northern California near the Oregon border, are known for their rugged terrain and biodiversity. This region is rich in coniferous forests, including the famous coastal redwoods.

Physiographic Regions of California
BASIN AND RANGE, GREAT BASIN
This region covers northeastern California and is characterized by alternating mountain ranges and flat valleys. It includes dry, arid basins and supports diverse wildlife.
BASIN AND RANGE, MEXICAN HIGHLAND
This section lies in southeastern California and stretches into Mexico. The terrain features arid, rocky highlands and desert valleys.
BASIN AND RANGE, SALTON TROUGH
The Salton Trough is an extension of the Basin and Range province, and is known for the Salton Sea, an inland saline lake located in the Colorado Desert region of Southern California.
BASIN AND RANGE, SONORAN DESERT
Part of the larger Sonoran Desert, this region spans southeastern California. It is a low-elevation desert with unique flora like the iconic saguaro cactus.
CASCADE-SIERRA MOUNTAINS, SIERRA NEVADA
This region includes the Sierra Nevada, which is home to California’s highest peaks, vast forests, and a range of habitats from alpine to montane.
CASCADE-SIERRA MOUNTAINS, SOUTHERN CASCADE MOUNTAINS
The southern part of the Cascade Range, including Lassen Peak, features volcanic landscapes, geothermal activity, and dense forests.
LOWER CALIFORNIAN
This region covers much of Southern California, characterized by warm, Mediterranean climates, coastal scrub, and chaparral ecosystems.
PACIFIC BORDER, CALIFORNIA COAST RANGES
This rugged coastal region extends along California’s Pacific coastline. It is characterized by mountainous terrain and diverse ecosystems, including coastal redwood forests.
PACIFIC BORDER, CALIFORNIA TROUGH
This region includes the Central Valley and its surrounding lowlands, forming one of the most productive agricultural areas in the world.
PACIFIC BORDER, KLAMATH MOUNTAINS
The Klamath Mountains, located in northern California near the Oregon border, are known for their rugged terrain and biodiversity.
PACIFIC BORDER, LOS ANGELES RANGES
This region includes the mountains surrounding the Los Angeles Basin, such as the Santa Monica and San Gabriel Mountains, providing a dramatic backdrop to the city.
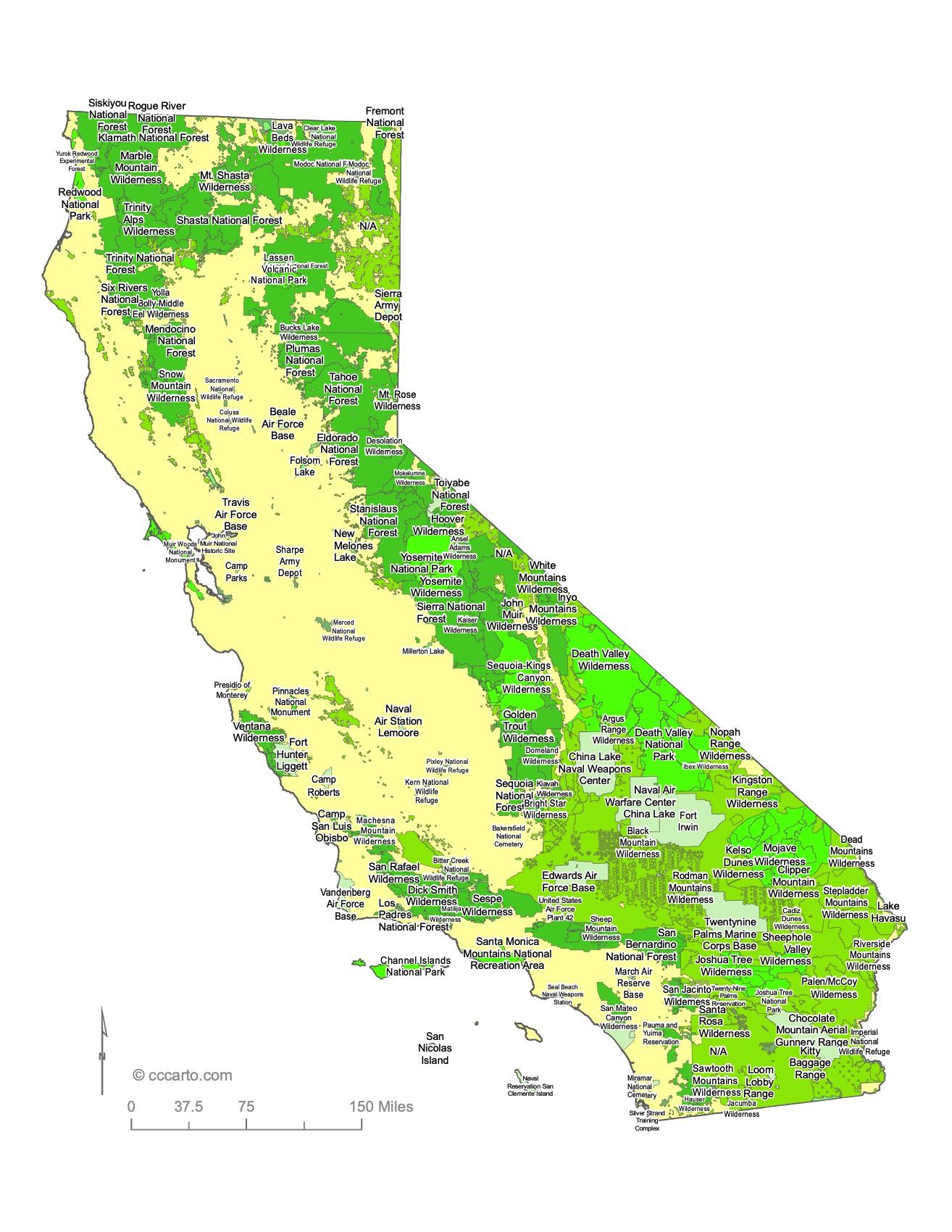
Notable Federal Lands: Some of the Largest and Most Fascinating Destinations in California
1. Yosemite National Park
Yosemite is one of California’s most famous national parks, known for its towering granite cliffs, waterfalls, and giant sequoia trees. It attracts millions of visitors each year.
2. Death Valley National Park
Located in eastern California, Death Valley is the hottest and driest place in North America, offering stark desert landscapes and unique geological features.
3. Sequoia and Kings Canyon National Parks
These two adjacent national parks are home to some of the world's largest trees, the giant sequoias, as well as stunning mountain landscapes and alpine scenery.
4. Joshua Tree National Park
Famous for its iconic Joshua Trees and rugged rock formations, this park offers a blend of two desert ecosystems: the Mojave and Colorado Deserts.
5. Lassen Volcanic National Park
Lassen Peak is one of the largest plug dome volcanoes in the world, and the park features a variety of geothermal features, including boiling springs and fumaroles.
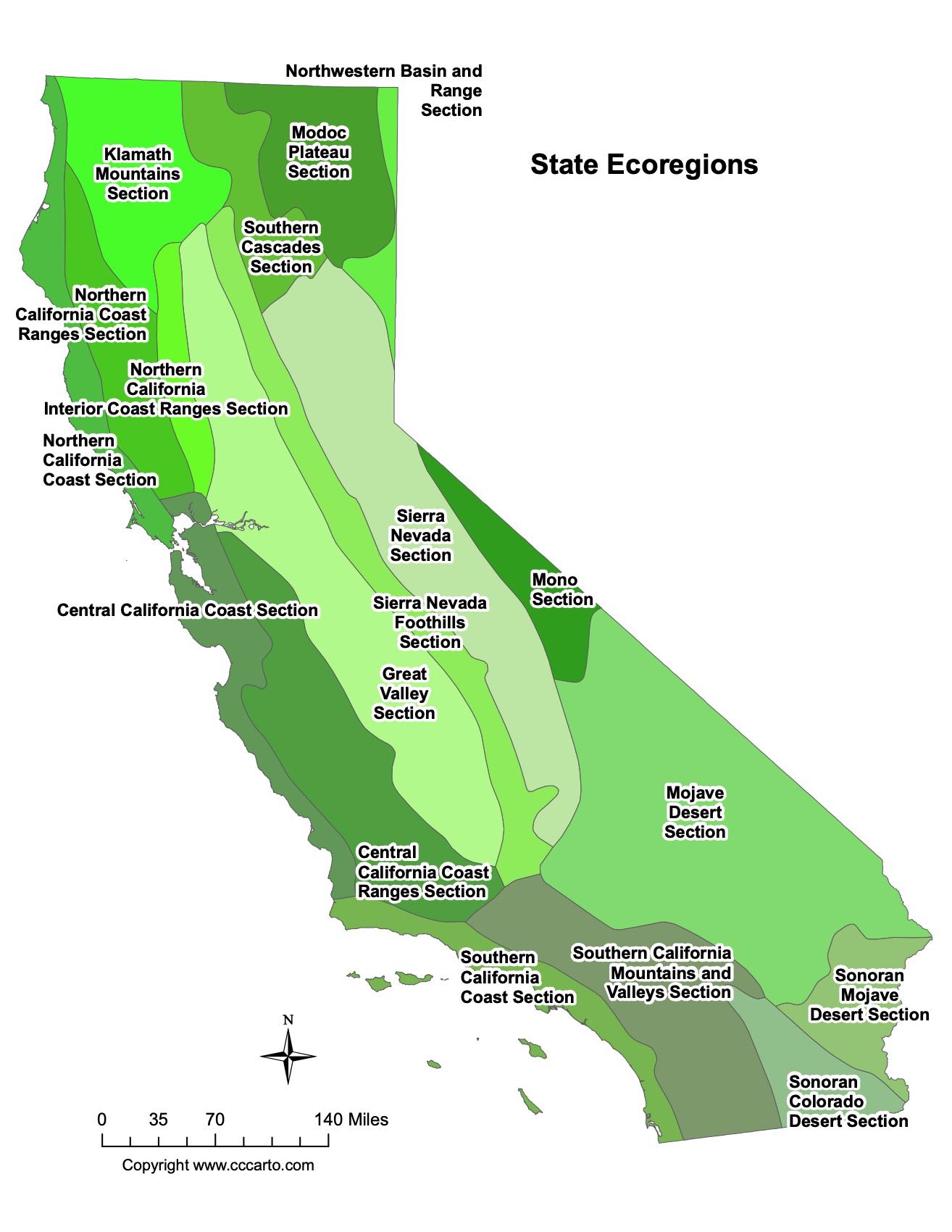
Ecoregions of California
Central California Coast Ranges Section
This ecoregion features rugged coastal mountains and rolling hills. It has a Mediterranean climate and supports diverse ecosystems, including chaparral and oak woodlands.
Central California Coast Section
Running along the central coast, this section includes lowlands, coastal dunes, and wetlands. It is home to rich agricultural lands and unique coastal species.
Great Valley Section
This ecoregion encompasses the fertile Central Valley, one of the most productive agricultural regions in the world, and supports vast grasslands, rivers, and wetlands.
Klamath Mountains Section
Known for its biological diversity, this section includes forested mountains and supports numerous endemic plant species and rich wildlife habitats.
Modoc Plateau Section
The Modoc Plateau is located in northeastern California and features volcanic landscapes, high desert, and forested lava flows, home to unique high-elevation species.
Mojave Desert Section
This ecoregion represents the driest and hottest desert environment in California, home to unique species such as the desert tortoise and diverse cacti.
Mono Section
Located in eastern California, this section includes high desert basins and the iconic Mono Lake, a saline soda lake that supports unique aquatic life.
Northern California Coast Ranges Section
This section features rugged mountains, coastal forests, and river systems. It includes the northern reaches of California’s coastal redwoods.
Northern California Coast Section
This ecoregion spans northern coastal areas and is known for its temperate rainforests, featuring towering redwoods and a cool, moist climate.
Northern California Interior Coast Ranges Section
Situated inland, this section includes forested mountain ranges and grasslands, providing important habitats for diverse plant and animal species.
Northwestern Basin and Range Section
This section covers northeastern California’s arid, mountainous terrain, featuring valleys and salt flats within the Great Basin.
Sierra Nevada Foothills Section
The foothills of the Sierra Nevada include rolling oak woodlands and chaparral ecosystems, transitioning from the Central Valley to the high mountain ranges.
Sierra Nevada Section
This section covers the higher elevations of the Sierra Nevada, including alpine meadows, coniferous forests, and glacier-carved valleys.
Sonoran Colorado Desert Section
Located in southeastern California, this ecoregion includes low-elevation deserts, home to unique flora like creosote bush and wildlife such as bighorn sheep.
Sonoran Mojave Desert Section
This section covers parts of both the Mojave and Sonoran Deserts, featuring diverse desert landscapes and ecosystems adapted to extreme aridity.
Southern California Coast Section
This section includes coastal plains and mountain ranges of Southern California, supporting chaparral, coastal sage scrub, and rare species such as the California gnatcatcher.
Southern Cascades Section
This ecoregion includes the southern part of the Cascade Range, with coniferous forests, volcanic features, and important watersheds.
