North Carolina State Maps
These maps show North Carolina's Counties, Cities, Federal Areas, Physiographic, and Ecoregions.
North Carolina Counties Interesting Facts
North Carolina’s 100 counties run from Outer Banks to Blue Ridge; Wake & Mecklenburg are largest.
- Number of counties: 100 — List
- First & last established: Colonial shires; last created Avery & Hoke (1911) — Newberry Atlas
- Highest & lowest county: Highest at Mt. Mitchell (Yancey); lowest Outer Banks (Dare) — USGS
- Most & least populated: Most: Wake; Least: Tyrrell
- Least & most developed (proxy): Most: Wake; Least: Tyrrell (links above)
- Most geographically diverse: Transylvania County (waterfalls, Blue Ridge)
- Strangest-shaped county: Currituck County (long OBX sliver)
- State’s Biggest Commodity: Broilers & hogs lead receipts. USDA ERS
- Largest Private Employer: Walmart (statewide). NC Commerce list
- Top 3 Non-English Languages: Spanish, Chinese, Vietnamese — DataUSA
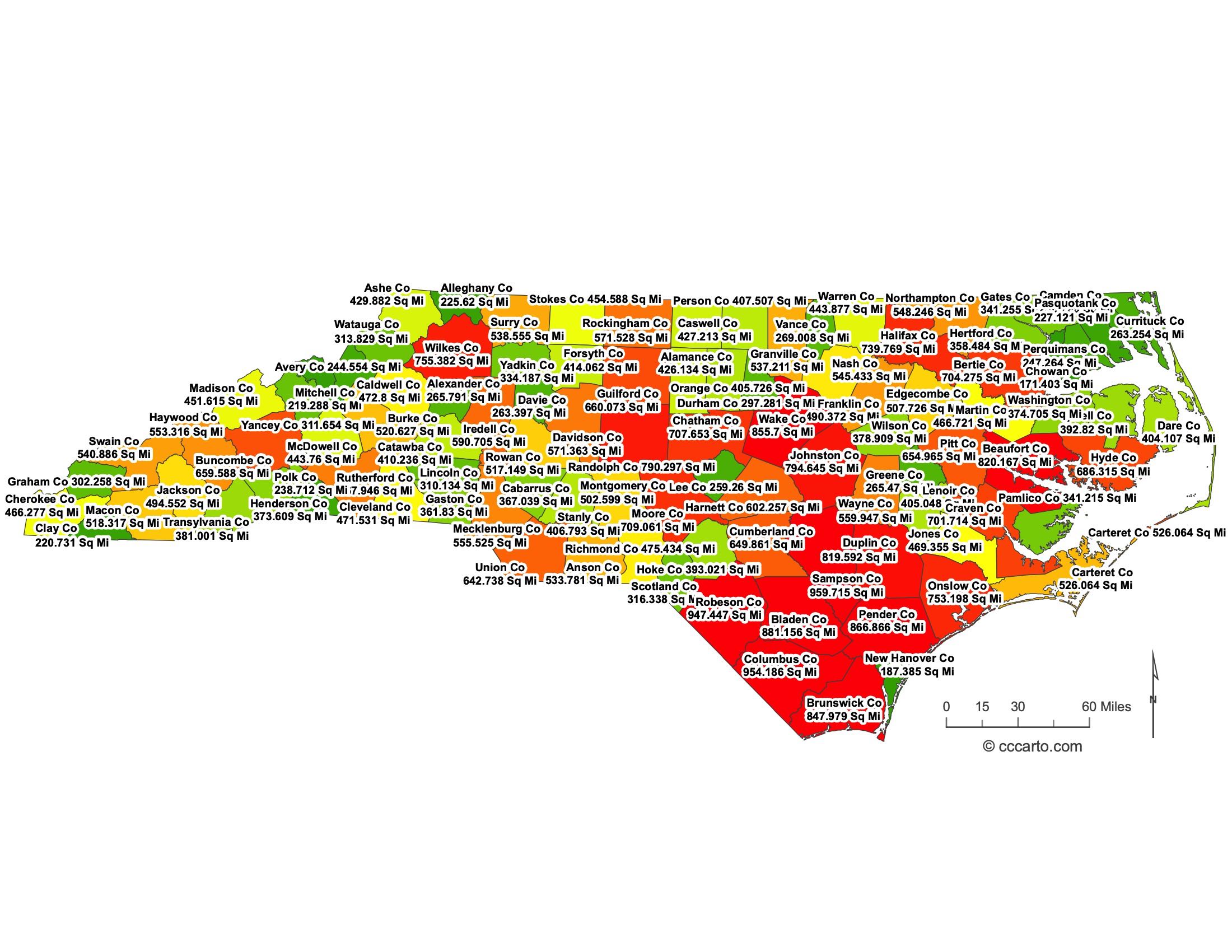
North Carolina State County Sizes Map
Smallest County in North Carolina State
Clay County: 220 sq miles
Largest County in North Carolina State
Robeson County: 947 sq miles
Mean and Median Area of Counties in North Carolina State
Mean Area: 544 sq miles
Median Area: 523 sq miles
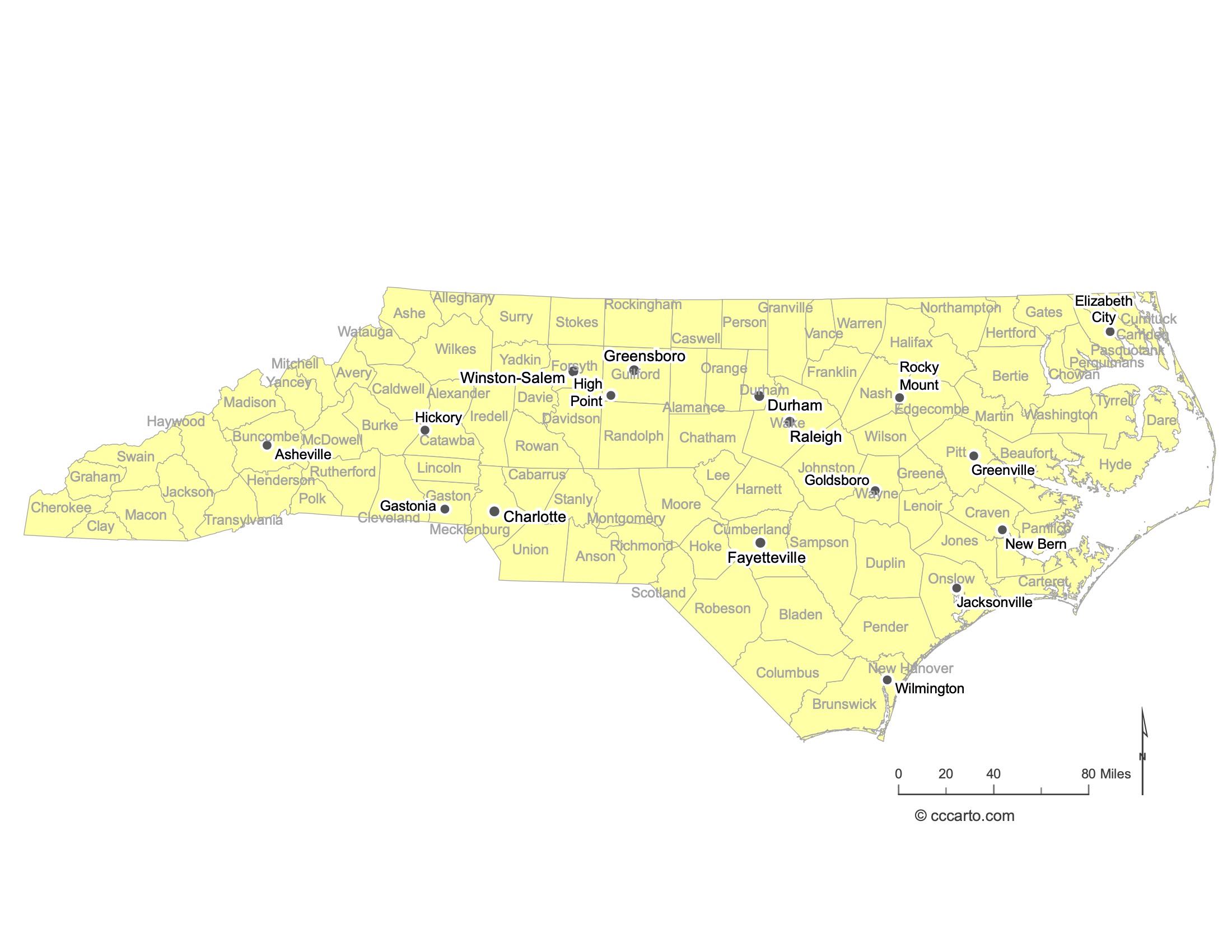
Major Cities of North Carolina State and Their Locations
In North Carolina, major cities are strategically located near coastal ports, river valleys, and historic transportation routes. Below are examples:
1. Coastal Cities
Wilmington: Located along the Cape Fear River, Wilmington has historically served as a significant port city with access to the Atlantic Ocean.
Morehead City: Situated along the Crystal Coast, Morehead City is known for its port facilities and commercial fishing industry.
2. Piedmont Cities
Charlotte: A major financial hub located in the Piedmont region, Charlotte is the largest city in North Carolina and serves as a key transportation and business center.
Raleigh: The state capital, Raleigh is known for its role in government and education, with numerous universities in the Research Triangle area.
3. Mountain Cities
Asheville: Nestled in the Blue Ridge Mountains, Asheville is a popular tourist destination known for its vibrant arts scene and outdoor recreation opportunities.
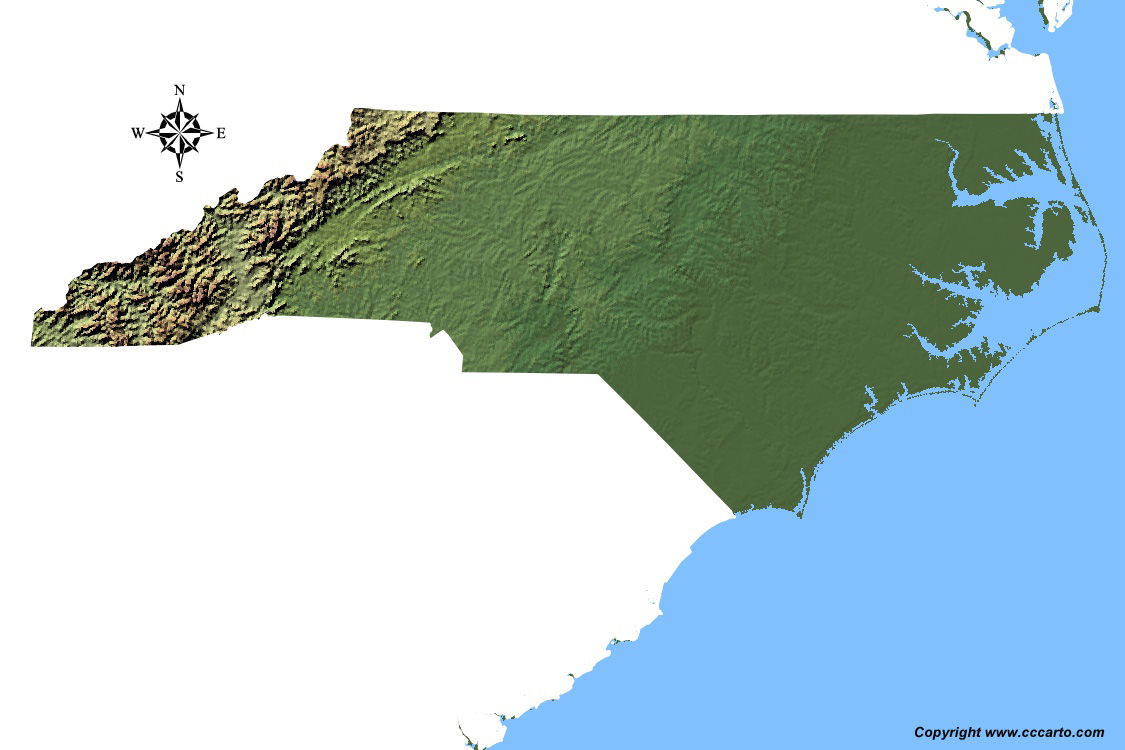
Topographic Tour of North Carolina
North Carolina offers diverse terrains shaped by its unique geography and natural features. From the Appalachian Mountains in the west to the Atlantic Coastal Plain in the east, the state presents a rich variety of landscapes.
1. Blue Ridge Mountains
The western edge of North Carolina is dominated by the Blue Ridge Mountains, part of the Appalachian Mountain chain. These mountains feature lush forests, high peaks, and scenic valleys, making them a popular destination for hiking, camping, and outdoor recreation.
2. Piedmont Region
The central Piedmont region is characterized by rolling hills, fertile valleys, and urban centers. This region is the heart of North Carolina's economic and cultural life, home to cities like Charlotte, Raleigh, and Greensboro.
3. Coastal Plain
The eastern part of the state consists of the Atlantic Coastal Plain, which includes low-lying flatlands, swamps, and estuaries. This region is known for its rich agricultural lands and access to the Atlantic Ocean through port cities like Wilmington.
4. Outer Banks
The Outer Banks are a series of narrow barrier islands off the coast of North Carolina. These islands separate the mainland from the Atlantic Ocean, creating a unique landscape of sand dunes, beaches, and marshes. The Outer Banks are popular for tourism, offering activities such as fishing, boating, and wildlife observation.
5. Great Dismal Swamp
Located in the northeastern part of the state, the Great Dismal Swamp is a vast wetland area that extends into Virginia. This region features dense forests, swamps, and wildlife habitats, offering visitors opportunities for hiking, canoeing, and birdwatching.
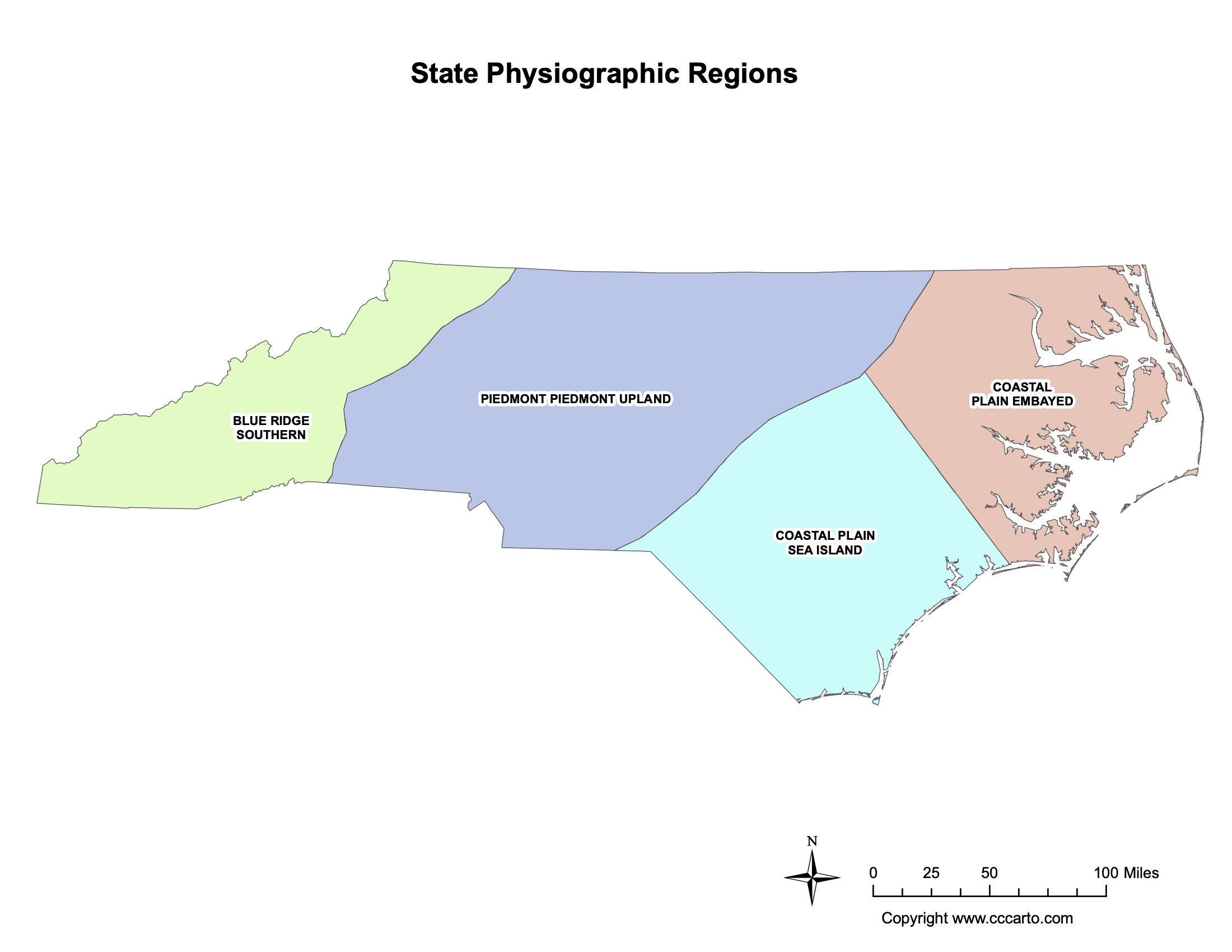
Physiographic Regions of North Carolina
Blue Ridge, Southern
This region encompasses the southern portion of the Appalachian Mountains, with rugged peaks and deep valleys, offering rich biodiversity and numerous outdoor recreational activities.
Coastal Plain, Sea Island
This region is characterized by barrier islands, sandy beaches, and tidal flats, forming a natural buffer between the Atlantic Ocean and the mainland.
Piedmont Upland
The Piedmont Upland is a region of rolling hills and fertile valleys, where many of North Carolina’s major cities and agricultural activities are located.
Coastal Plain, Embayed
The Embayed Coastal Plain features low-lying wetlands and estuaries along the Atlantic coast, with important ecosystems supporting diverse wildlife.
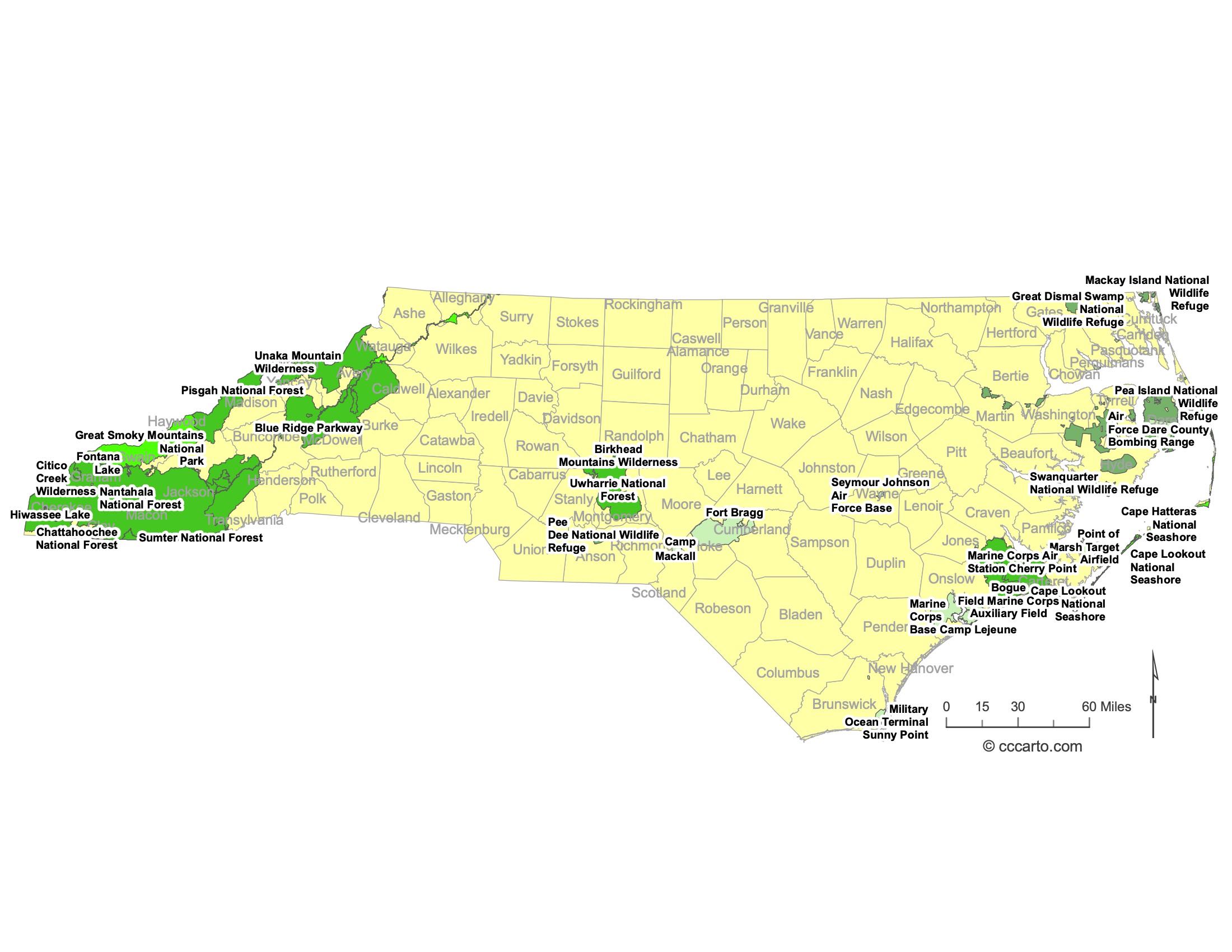
Notable Federal Lands: Some of the Largest and Most Fascinating Destinations in North Carolina
1. Great Smoky Mountains National Park
Straddling the border between North Carolina and Tennessee, Great Smoky Mountains National Park is one of the most visited national parks in the United States. It is known for its ancient mountains, diverse wildlife, and stunning scenic views.
2. Cape Hatteras National Seashore
Cape Hatteras is a long stretch of protected coastline along the Outer Banks, featuring sandy beaches, lighthouses, and opportunities for fishing, birdwatching, and water sports.
3. Croatan National Forest
Located in eastern North Carolina, the Croatan National Forest offers a mix of pine forests, saltwater estuaries, and unique habitats like pocosins and bogs. It is a prime location for hiking, camping, and wildlife observation.
4. Pisgah National Forest
Covering over half a million acres in the Appalachian Mountains, Pisgah National Forest is renowned for its dense hardwood forests, waterfalls, and scenic hiking trails. It's popular for camping, hiking, and mountain biking.
5. Uwharrie National Forest
Located in the central part of North Carolina, Uwharrie National Forest is known for its gently rolling terrain, making it ideal for hiking, horseback riding, and camping. The forest is a popular destination for off-roading enthusiasts.
6. Pea Island National Wildlife Refuge
Situated on the Outer Banks, Pea Island National Wildlife Refuge is a haven for birdwatchers and wildlife enthusiasts. The refuge offers opportunities for kayaking, birdwatching, and nature photography, especially during bird migration seasons.
7. Alligator River National Wildlife Refuge
This vast refuge in eastern North Carolina is home to a diverse range of wildlife, including black bears, red wolves, and a variety of migratory birds. It offers excellent opportunities for wildlife viewing, kayaking, and nature tours.
8. Mattamuskeet National Wildlife Refuge
Mattamuskeet NWR is known for its shallow, freshwater lake that attracts thousands of migratory birds during the winter. It’s a prime spot for birdwatching, fishing, and photography.
9. Cape Lookout National Seashore
Located along the southern Outer Banks, Cape Lookout National Seashore is known for its pristine beaches, historic lighthouse, and opportunities for camping, boating, and birdwatching. The seashore's undeveloped barrier islands provide a tranquil escape from the busier coastal areas.
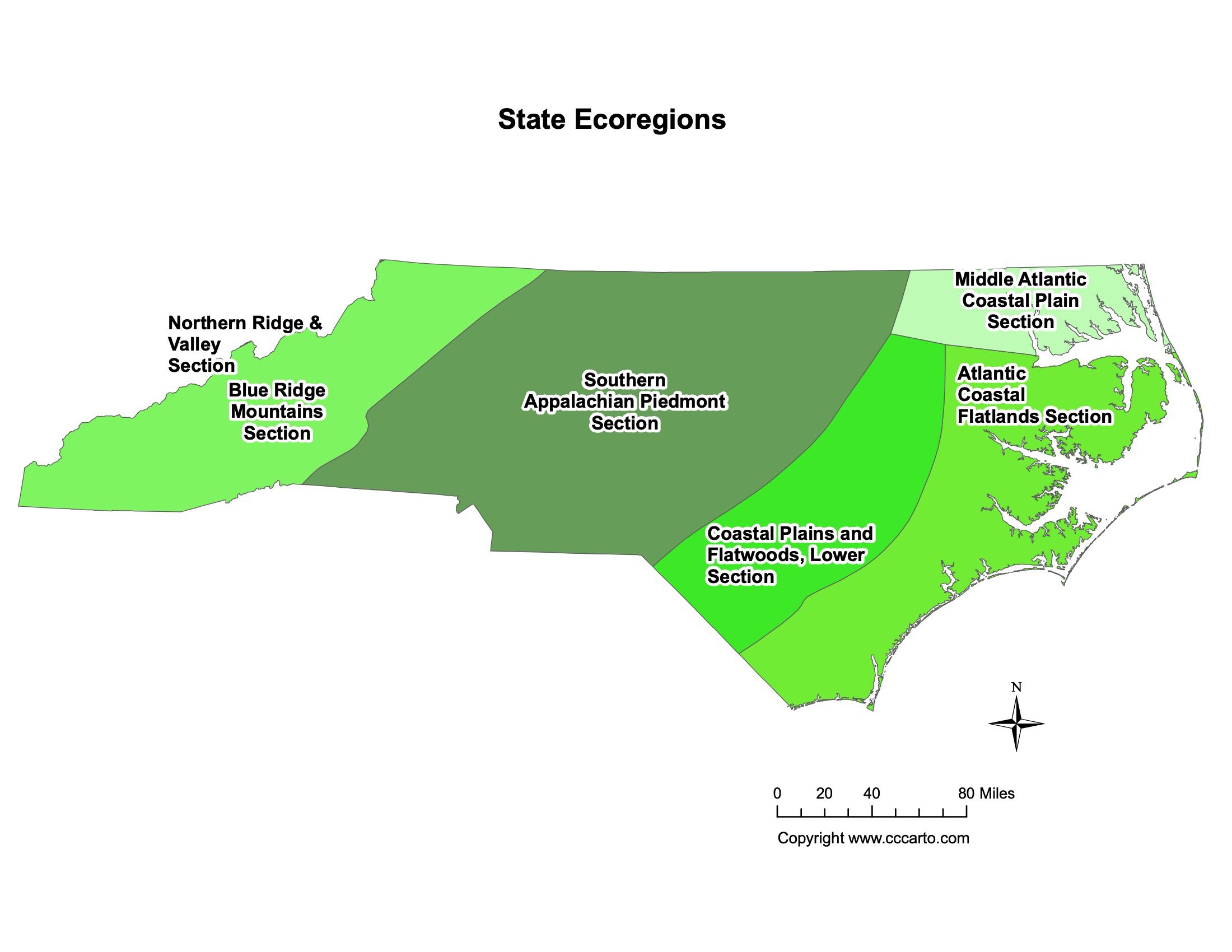
Ecoregions of North Carolina
Atlantic Coastal Flatlands Section
This region includes flat, low-lying areas along the coast, known for their rich ecosystems and salt marshes.
Blue Ridge Mountains Section
The Blue Ridge Mountains in western North Carolina are characterized by dense forests, high peaks, and a variety of wildlife species.
Coastal Plains and Flatwoods, Lower Section
This area features flatlands and forests near the coast, with important habitats for both marine and terrestrial species.
Middle Atlantic Coastal Plain Section
This section of the coastal plain includes agricultural lands, forests, and wetlands, providing key resources for wildlife and agriculture.
Northern Ridge & Valley Section
This region includes rolling valleys and ridges that form part of the Appalachian Mountain system, supporting diverse ecosystems and agricultural activities.
Southern Appalachian Piedmont Section
The Southern Appalachian Piedmont is characterized by gently rolling hills and valleys, where much of the state’s agriculture and urban development occur.
